Allows users to include binary logic in their queries.
With this functionality, users:
Apply bitwise AND, OR, XOR and NOT operations on values.
Shift bit to left and right in binary digits.
Count the number of 1 bits in a value’s binary representation.
Generic syntax:
| process eval("x=binary_and(1,1)")
Accepts two or more integers and applies binary AND on them.
Example:
| process eval("and_value=binary_and(1,1)")
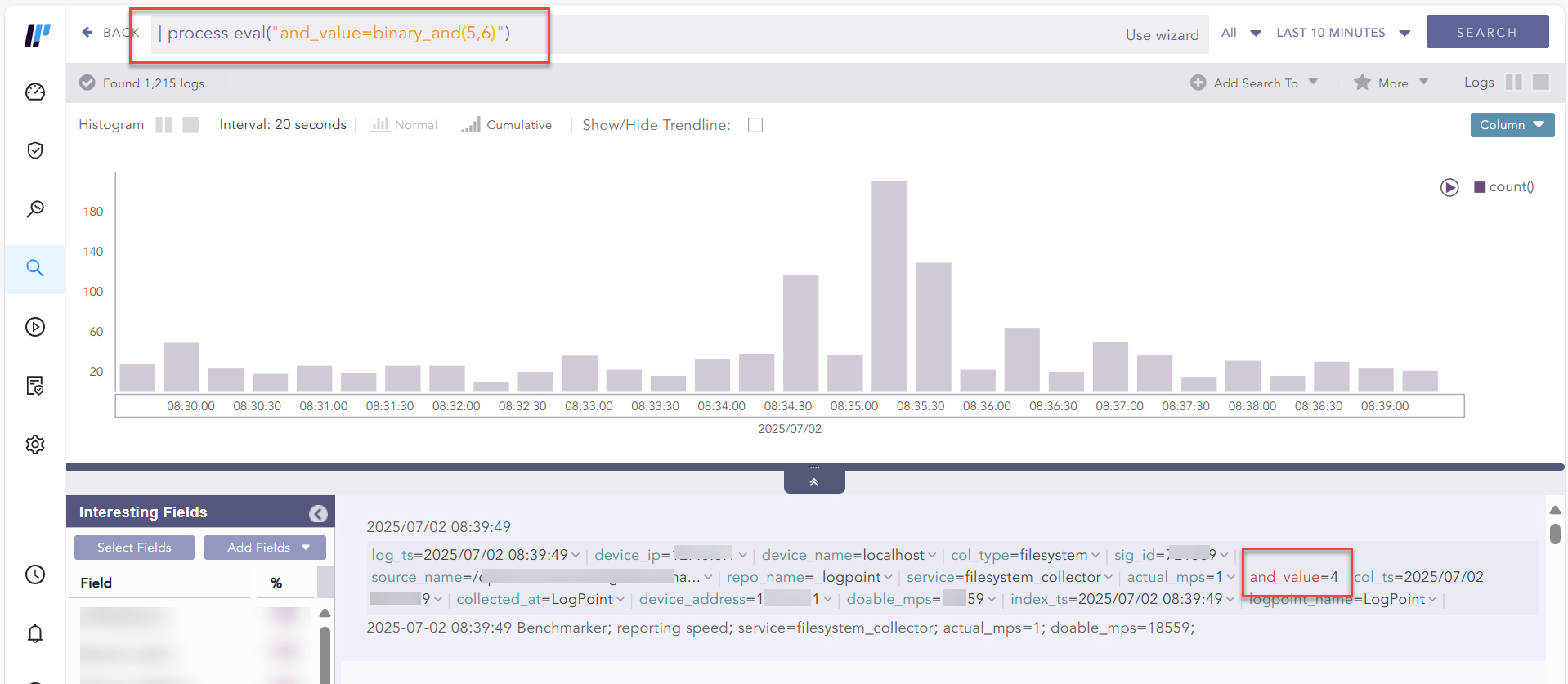
Using binary_and function¶
Here, each bit of the first operand is compared with the corresponding bit of the second operand. If both bits are 1, corresponding result bit is set to 1, otherwise the corresponding result bit is set to 0.
Accepts two or more integers and applies binary OR on them.
Example:
| process eval("or_value=binary_or(0,6)")
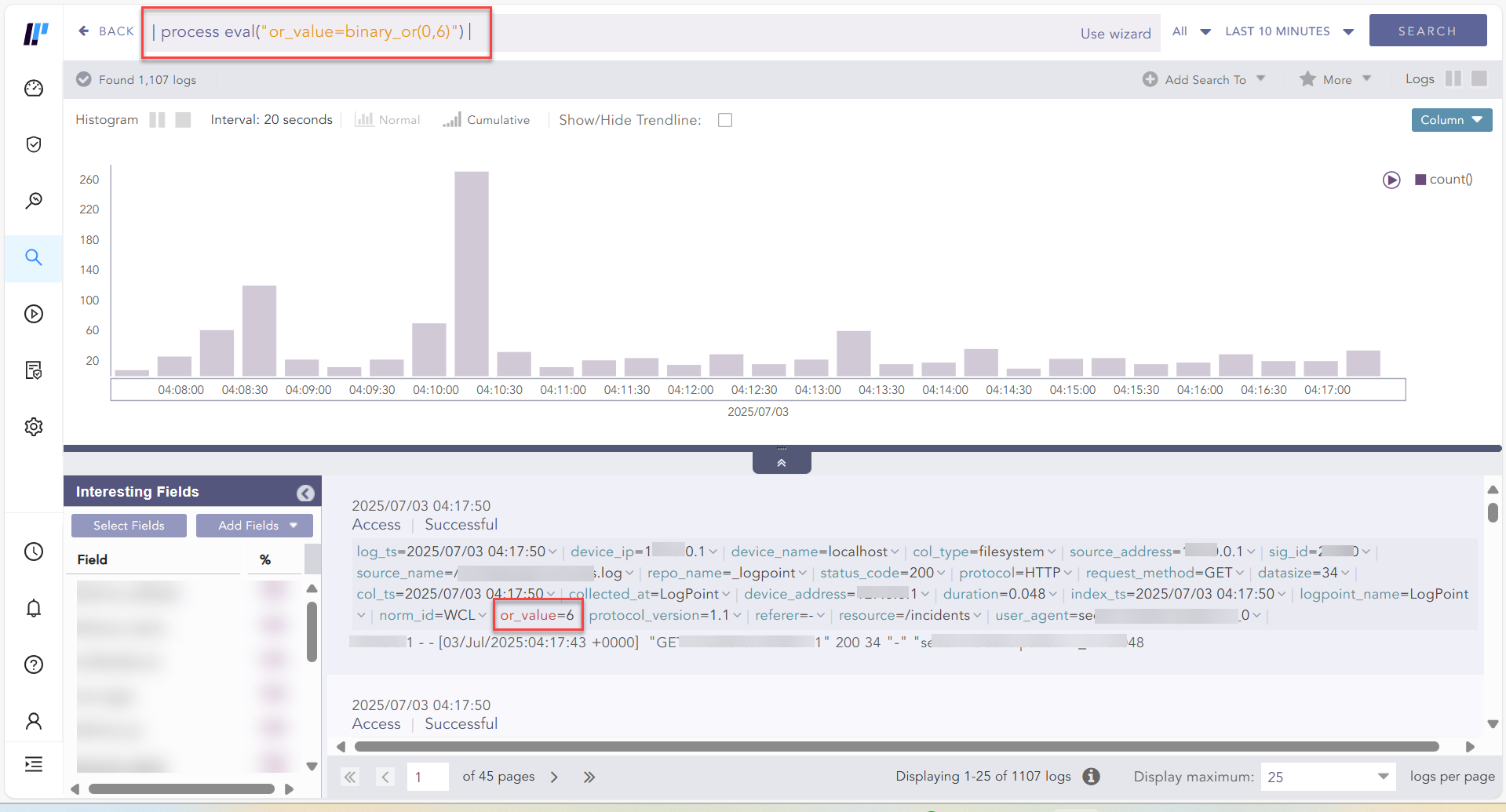
Using binary_or function¶
Here, each bit of the first operand is compared with the corresponding bit of the second operand. If both bits are 0, corresponding result bit is set to 0, otherwise the corresponding result bit is set to 1.
Takes a non-negative integer as an argument and inverts every bit in the binary representation of that number.
Example:
| process eval("not_value=binary_not(0)")
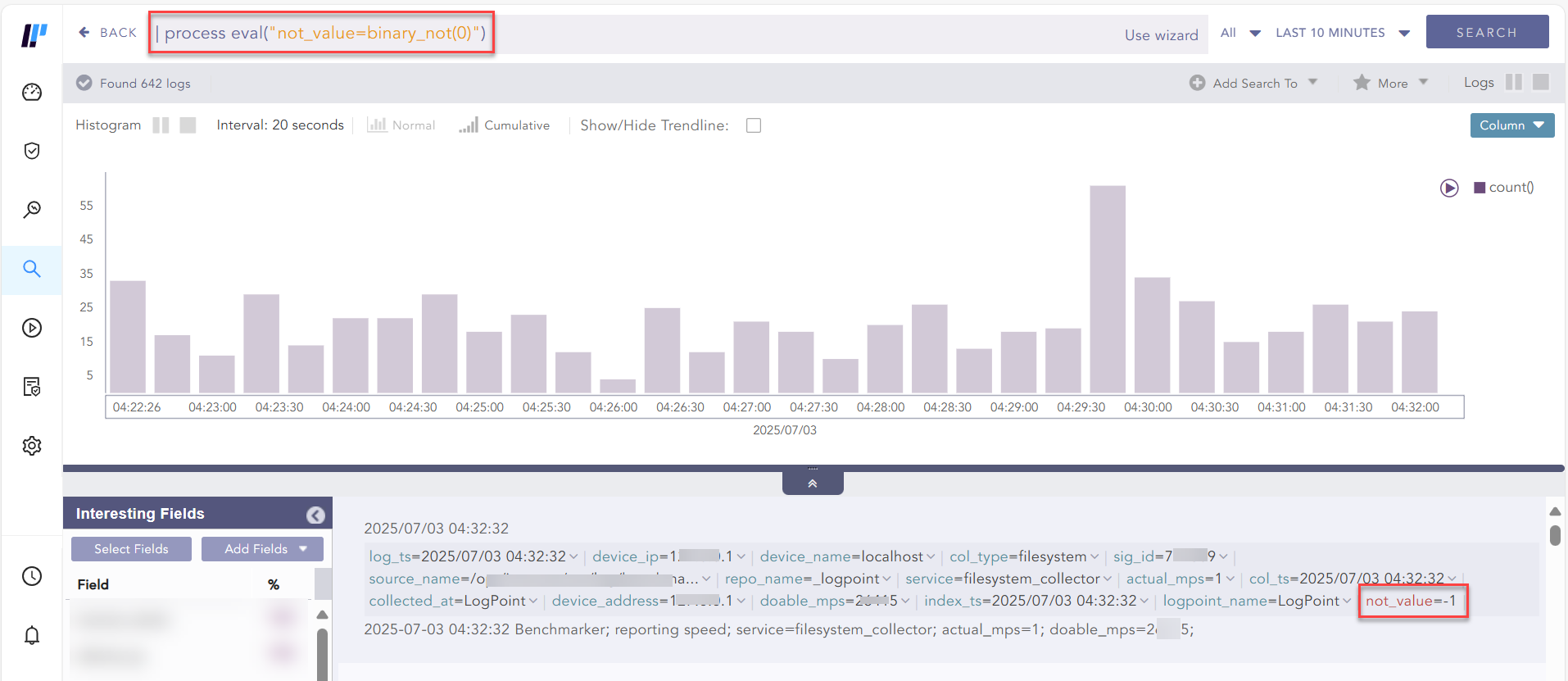
Using binary_not function¶
Takes two or more nonnegative integers as arguments and sequentially applies bitwise XOR operations on each of the given arguments.
Example:
| process eval("xor_value=binary_xor(5,10)")
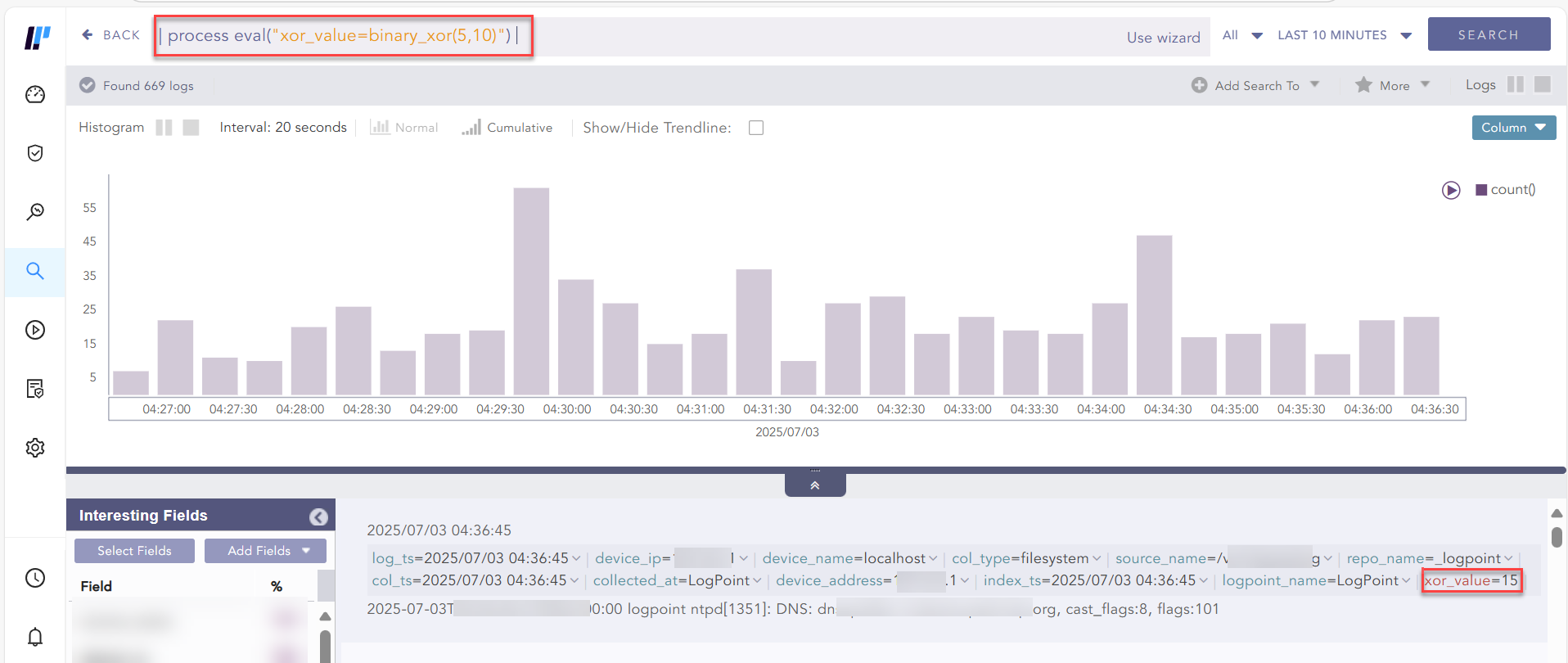
Using binary_xor function¶
Takes two valid nonnegative integers as arguments and shifts the binary representation of the first integer over to the right by the specified shift offset amount.
Example:
| process eval("right_shift_value=binary_right_shift(9,1)")
Using binary_right_shift function¶
We are glad this guide helped.
Please don't include any personal information in your comment
Contact Support