An Arithmetic expression is the combination of numbers, operators and variables that results in a numeric value.
Generic Syntax:
| process eval("identifier = first_operand arithmetic_operator second_operand")
This function accepts numerical values as inputs for addition and generates the output in the destination field (identifier).
Example:
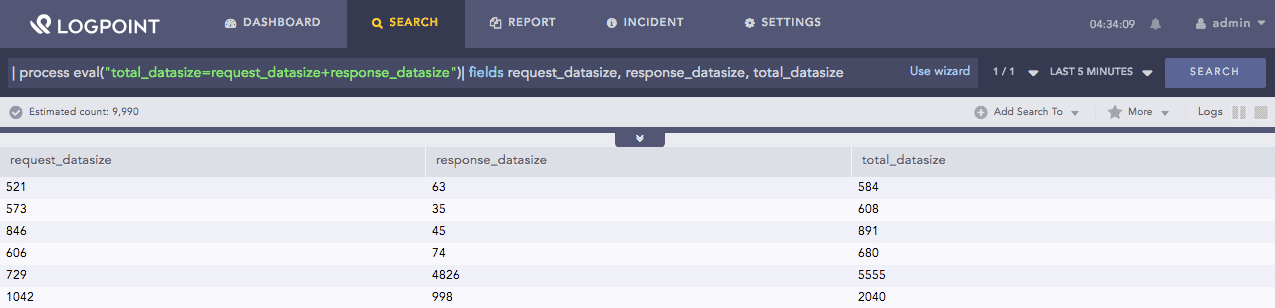
| process eval("total_datasize=request_datasize+response_datasize")
| fields request_datasize, response_datasize, total_datasize
The above example calculates the value of the total_datasize identifier by adding the values of the request_datasize and response_datasize fields.
The fields command displays the corresponding values of all the three fields in a tabular form.
Addition function¶
Note
The Addition function also accepts string values as inputs and returns the concatenation of values as the output.
This function accepts numerical values as inputs for subtraction and generates the output in the destination field (identifier).
Example:
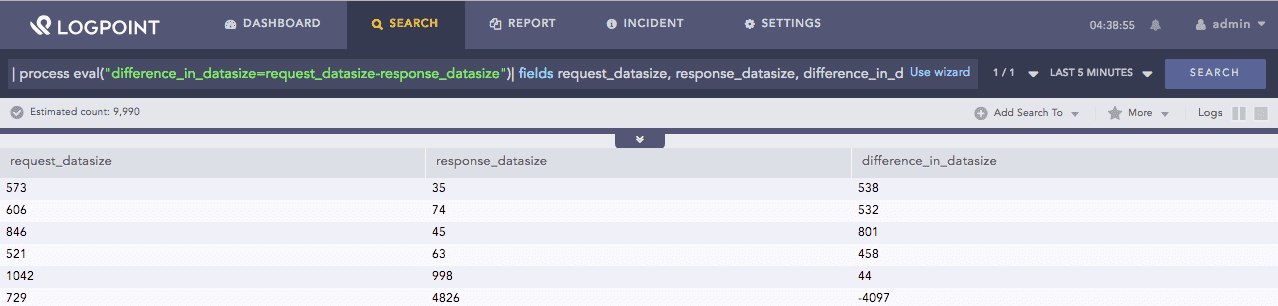
| process eval("difference_in_datasize=request_datasize-response_datasize")
| fields request_datasize, response_datasize, difference_in_datasize
The above example calculates the value of the difference_in_datasize identifier by subtracting the values of the response_datasize field from the request_datasize field.
The fields command displays the corresponding values of all the three fields in a tabular form.
Subtraction function¶
This function accepts numerical values as inputs for multiplication and generates the output in the destination field (identifier).
Example:
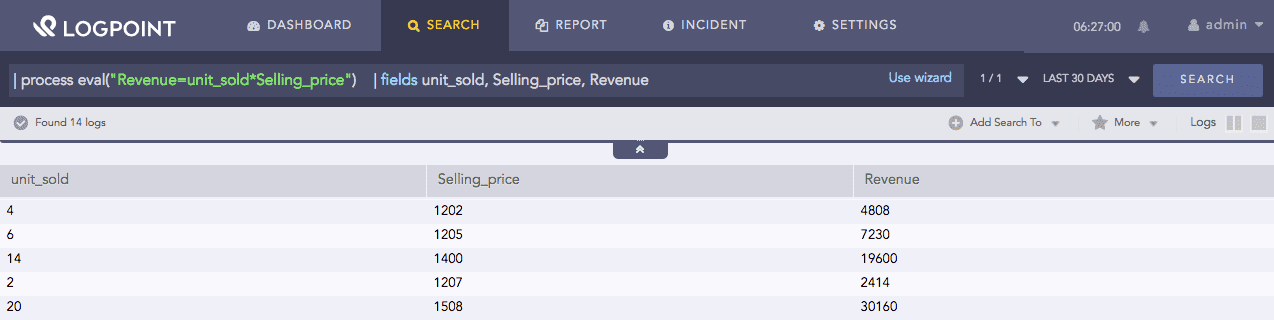
| process eval("Revenue=unit_sold*Selling_price")
| fields unit_sold, Selling_price, Revenue
The above example calculates the value of the Revenue identifier by multiplying the values of the unit_sold and Selling_price fields.
The fields command displays the corresponding values of all the three fields in a tabular form.
Multiplication function¶
This function accepts numerical values as inputs for the division and generates the output in the destination field (identifier).
Example:
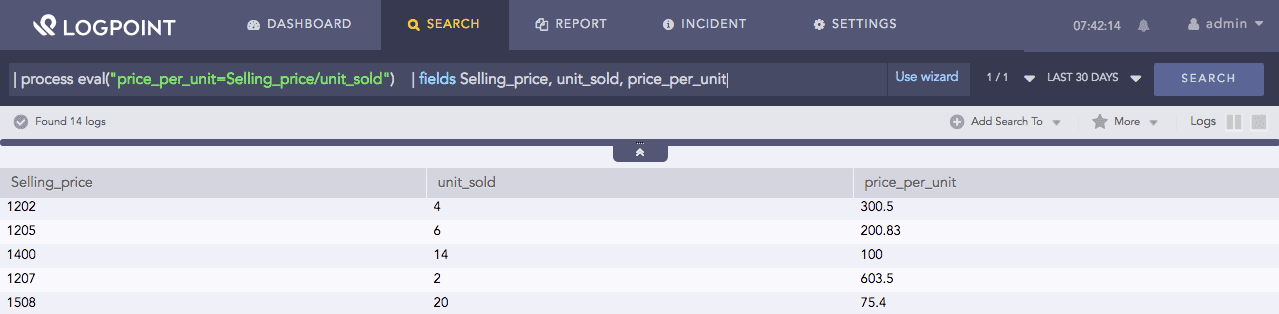
| process eval("price_per_unit=Selling_price/unit_sold")
| fields Selling_price, unit_sold, price_per_unit
The above example calculates the value of the price_per_unit identifier by dividing the values of the unit_sold and Selling_price fields.
The fields command displays the corresponding values of all the three fields in a tabular form.
Division function¶
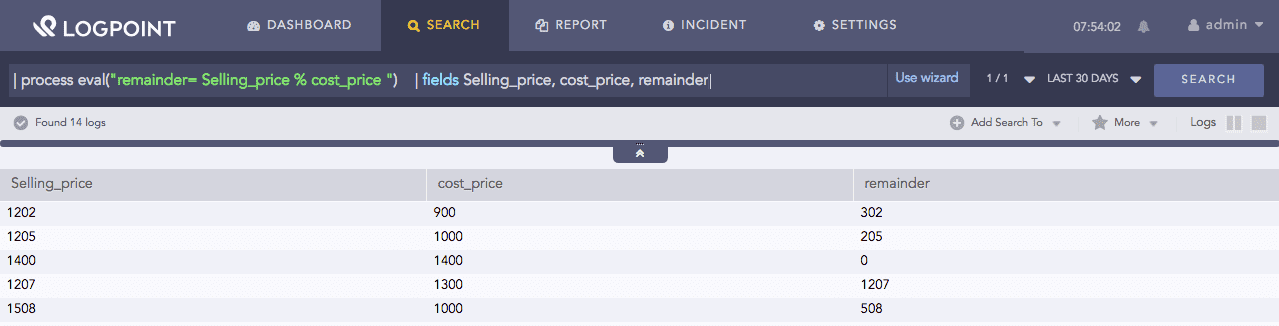
This function accepts numerical values as inputs for the division and generates the remainder of the division as the output in the destination field (identifier).
Example:
| process eval("modulo= Selling_price % cost_price ")
| fields Selling_price, cost_price, remainder
The above example calculates the value of the modulo identifier by finding the remainder after dividing the value of the Selling_price field by cost_price field.
The fields command displays the corresponding values of all the three fields in a tabular form.
Modulus function¶
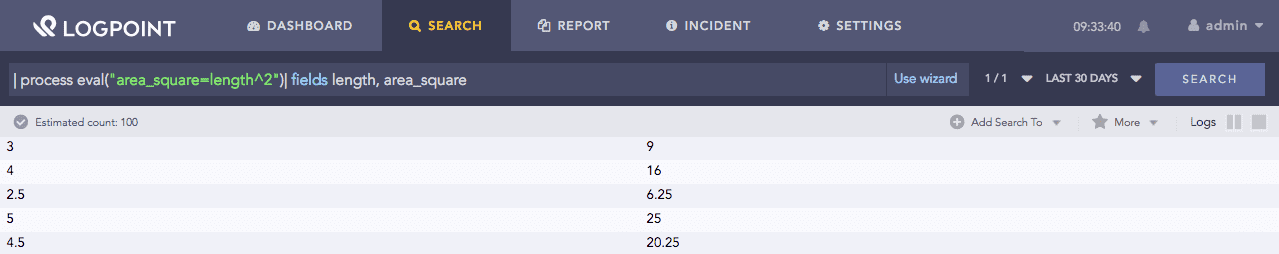
This function accepts numerical values as inputs for the power operation and generates the output in the destination field (identifier).
Example:
| process eval("area_square=length^2")
| fields length, area_square
The above example calculates the value of the area_square identifier by squaring the value of the length field.
The fields command displays the corresponding values of the two fields in a tabular form.
Power function¶
We are glad this guide helped.
Please don't include any personal information in your comment
Contact Support