Parsers extract individual logs from the incoming data and forward them for further processing in the log collection pipeline.
Collectors and fetchers use parsers to process the collected log. In addition to built-in, default parsers you can create your own. The provided regex pattern in the parser splits the message into individual log entries.
Parsers¶
Note
Since the Line parser splits logs greater than 12 KB into individual logs of 12 KB, the disk space can fill up quickly while receiving larger log files. You can monitor disk usage from System Monitor.
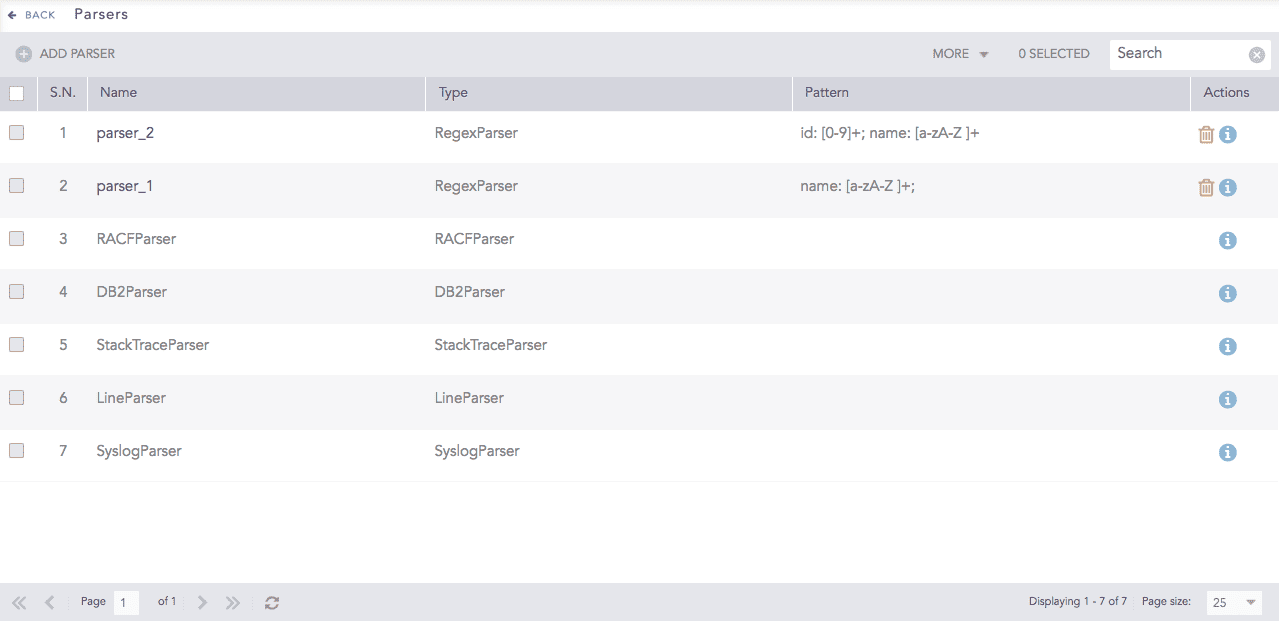
Go to Settings >> Configuration from the navigation bar and click Parsers.

Parsers¶
Click Add Parser.
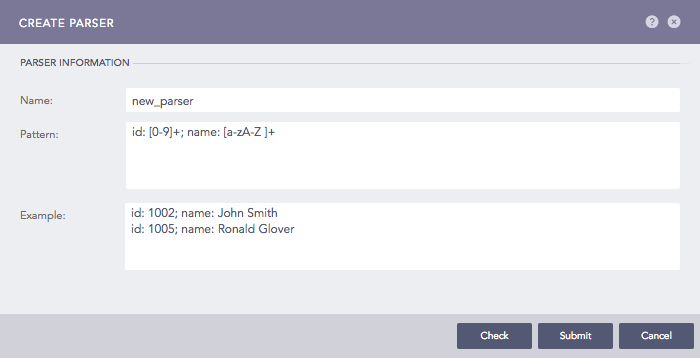
Addition of a Parser¶
Enter Name, Pattern, and Example.
Click Check to verify if the pattern matches the examples.
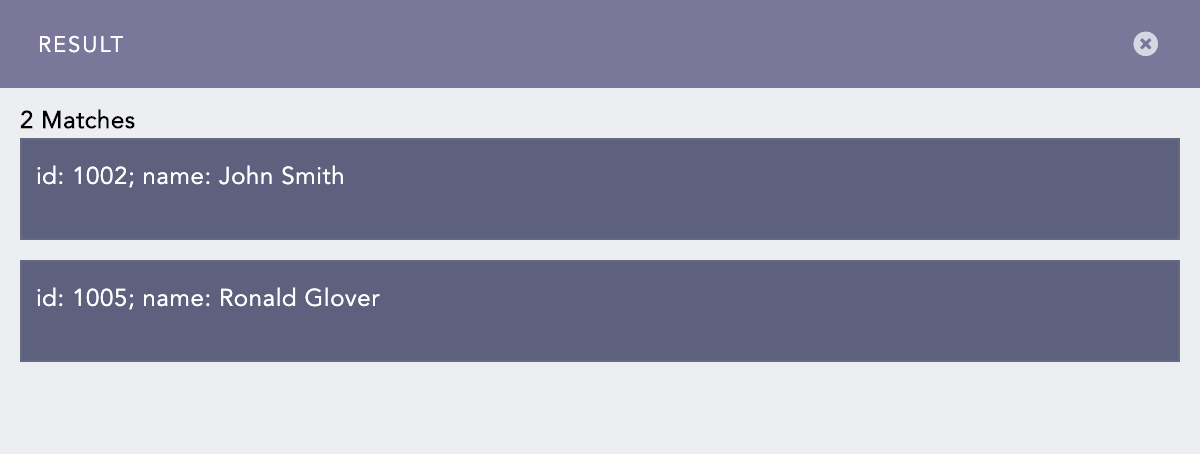
Pattern and Examples Check¶
Click Submit.
Now, apply the parser to the collection devices, i.e., collectors and fetchers.
Go to Settings >> Configuration from the navigation bar and click Parsers.
Click the Name of the required parser and update the information. You cannot edit the name of a parser.
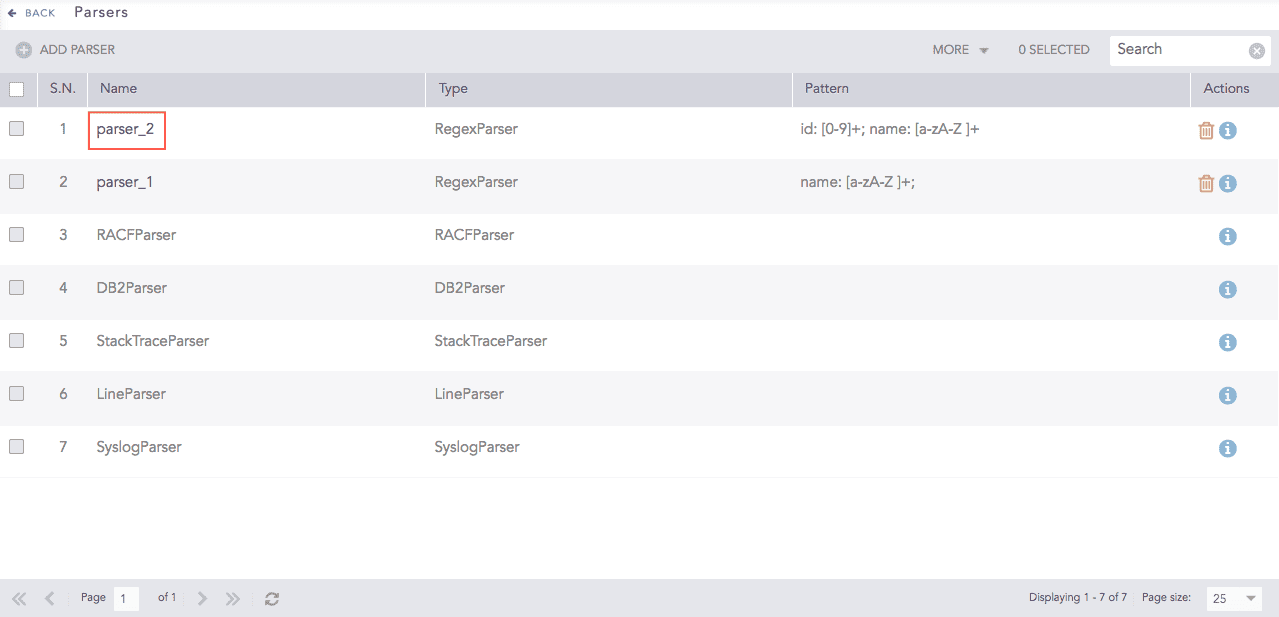
Parsers¶
Click the Check button to verify if the pattern matches the examples.
Click Submit.
Note
Click the ? icon near the top-right corner for context-sensitive help.
Go to Settings >> Configuration from the navigation bar and click Parsers.
Click the Delete icon under Actions.
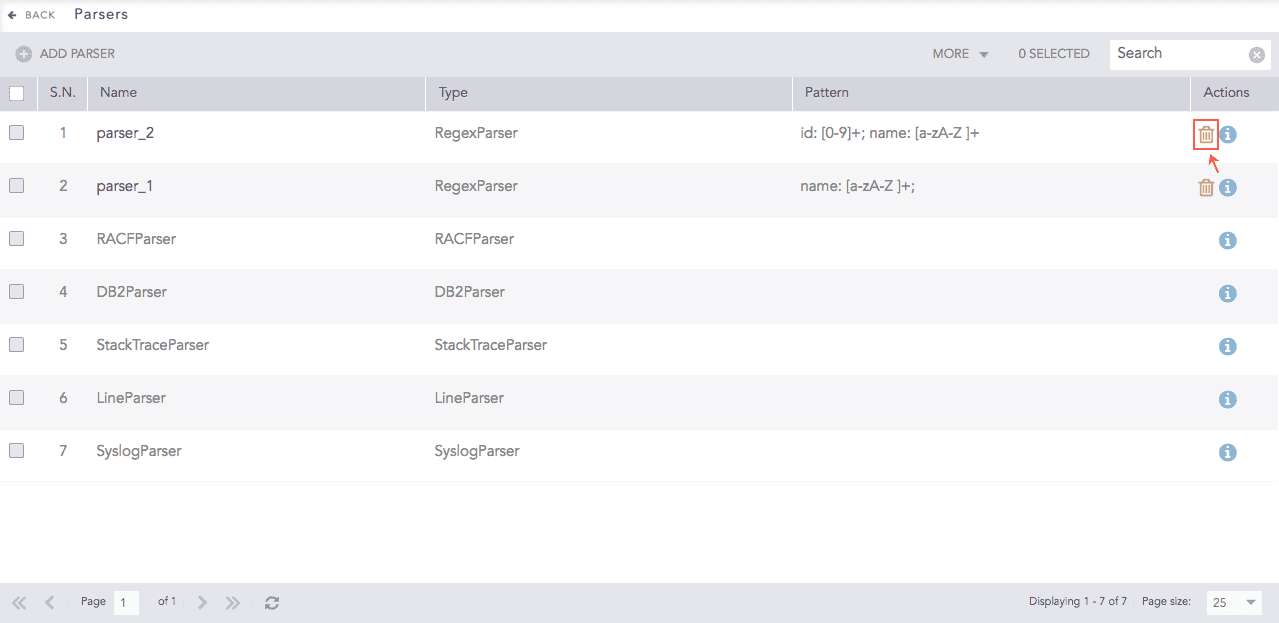
Parsers¶
To delete multiple parsers, select the parsers, click More and choose Delete Selected.
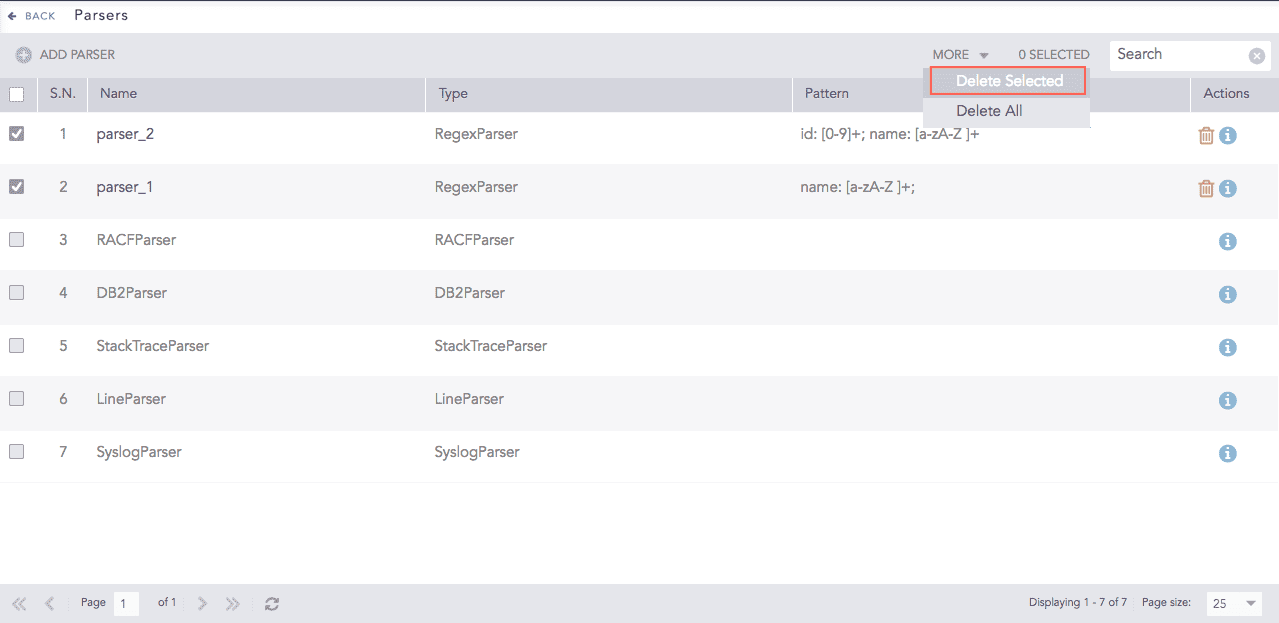
Parsers¶
To delete all the parsers, click More and choose Delete All.
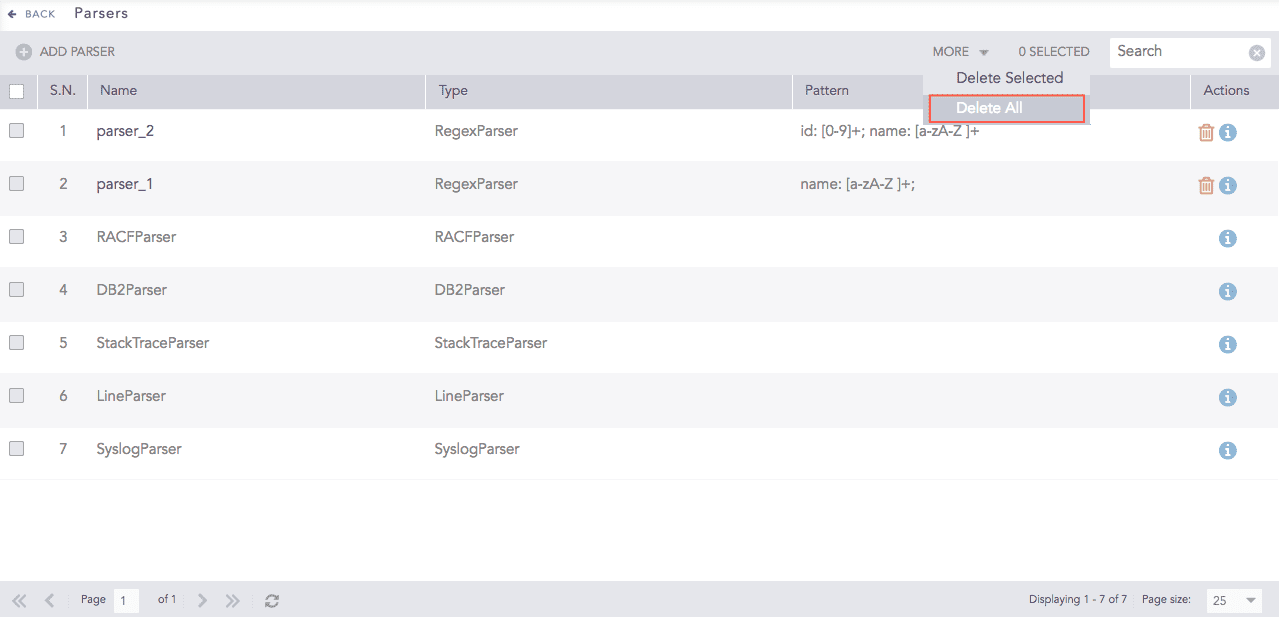
Parsers¶
Click Yes to confirm deletion.
Logpoint provides the following parsers you can use to parse some standarized log formats.
Splits each line in the incoming data into individual logs. If the size of the input message is larger than 12 KB, the message is split into individual logs.
Example:
Line parser splits the following type of log entries into two seperate logs:
Apr 28 08:58:18 EventCode=5156 EventType=0 Keywords=Audit Success Message=A connection permitted. Application Name: App Direction: Inbound Source Address: 21.21.3.133 Source Port: 80 Destination Address: 21.21.3.132 Destination Port:444
Apr 28 08:58:18 EventCode=5156 EventType=0 Keywords=Audit Success Message=A connection permitted. Application Name: App Direction: Inbound Source Address: 21.21.3.133 Source Port: 80 Destination Address: 21.21.3.132 Destination Port:6161
Splits multiple syslog messages into individual logs using the newline character. If the size of the input message is larger than the Message Length set from Syslog, the message is split into individual log by that length.
Example:
Syslog parser splits the following type of log entries separated by newline into two seperate logs:
<135>Apr 28 08:58:18 LogName=Security SourceName=Security audit. EventCode=5156 EventType=0 TaskCategory=Connection Keywords=Audit Success Message=A connection permitted. Process ID: 41 Application Name: App Direction: Inbound Source Address: 21.21.3.133 Source Port: 80 Destination Address: 21.21.3.132 Destination Port:444 \n <165>Apr 28 08:58:18 LogName=Security12 SourceName=Security audit1. EventCode=5156 EventType=0 TaskCategory=Connection Keywords=Audit Success Message=A connection permitted. Process ID: 41 Application Name: App Direction: Inbound Source Address: 21.21.3.133 Source Port: 80 Destination Address: 21.21.3.132 Destination Port:6161
Splits multiple syslog messages written in multiple lines into individual logs. It uses PRI (Priority Value), a numerical value enclosed in angle brackets “<>”, to split the messaage.
Example:
Multi Line Syslog parser splits the following type of log entries into three seperate logs:
<135>Apr 28 08:58:18
LogName=Security
SourceName=Security audit.
EventCode=5156
EventType=0
TaskCategory=Connection
Keywords=Audit Success
Message=A connection permitted.
Process ID: 41
Application Name: App
Direction: Inbound
Source Address: 21.21.3.133
Source Port: 80
Destination Address: 21.21.3.132
Destination Port:444
<165>Apr 28 08:58:18
LogName=Security12
SourceName=Security audit1.
EventCode=5156
EventType=0
TaskCategory=Connection
Keywords=Audit Success
Message=A connection permitted.
Process ID: 41
Application Name: App
Direction: Inbound
Source Address: 21.21.3.133
Source Port: 80
Destination Address: 21.21.3.132
Destination Port:6161
<161>Mar 19 11:38:18
LogName=Security123
SourceName=Security audit 123.
EventCode=5156
EventType=0
TaskCategory=Connection
Keywords=Audit Success
Message=A connection permitted.
Process ID: 4
Application Name: App
Direction: Inbound
Source Address: 21.21.3.133
Source Port: 80
Destination Address: 21.21.3.132
Destination Port:6161
Splits logs from multiple email services like Exim, Qmail, Cisco Ironport, and Postfix MTA. Email parser can only be used with Syslog collector.
Splits logs coming from Proofpoint’s Email Protection service.
Splits logs from IBM DB2 servers.
Splits logs from Resource Access Control Facility (RACF) devices.
Processes comma-separated values from a file. CSVParser can only be used with file-based collectors and fetchers.
Processes JSON lines from a file. JSONLineParser can only be used with file-based collectors and fetchers.
In addition to these parsers, Logpoint has default parsers specific to integrations. For more details, search for specific parsers in the ServiceDesk.
We are glad this guide helped.
Please don't include any personal information in your comment
Contact Support